Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
It is one of the most common a non-destructive testing (NDT) method where sound waves of high frequency(ranges from 1 MHZ TO 50MHZ) waves are transmitted into the material being tested are used to detect surface and sub-surface flaws. The sound waves travel through the materials with some attenuation of energy and are reflected at interfaces. The reflected beam is characterized to define the presence and location of flaws.
Ultrasonic waves are almost completely reflected at metal gas interfaces. Partial reflection occurs at metal liquid or metal solid interfaces, with the specific percentage of reflected energy depending mainly on the ratios of certain properties of the matter on opposite sides of the interface.
Cracks, laminations, shrinkage, cavities, bursts, flakes, pores, bonding faults and other discontinuities that can act as metal-gas interfaces can be easily detected. Inclusions and other inhomogenities in the metal being inspected can also detected by causing partial reflection or scattering of the ultrasonic waves, or by producing some other detectable effect on the ultrasonic waves.
Most of the ultrasonic inspection instruments detect flaws by monitoring one or more of the following:
1. Reflection of energy from metal-gas interfaces, metal-liquid interfaces or discontinuities within the metal itself
2. Time of transit of a sound wave through the test piece from the entrance point at the sending (transmitting) transducer to the exit point at the receiving transducer, and
3. Attenuation of the beam of sound waves by absorption and scattering within the test piece.
Application
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is used for quality control and materials testing in all major industries (power, oil&gas, foundry etc.). This includes Ultrasonic testing of castings, forgings, plates, extruded components, weld joints, production of steel, aluminum and titanium, fabrication of structures such as air frames, pressure vessels, ships, bridges, motor vehicles, machinery and jet engines. In service ultrasonic testing for preventive maintenance is used for detecting impending failure of pipelines, vessels, tank. The flaws to be detected include voids, cracks, inclusions, pipe, laminations, bursts and flakes. They may be inherent in the raw materials, may result from fabrication and heat treatment, or may occur in service from fatigue, corrosion or other causes. Ultrasonic testing can also be used to measure thickness of metal sections during manufacturing and maintenance inspections.
Advantages
1. It is sensitive to both surface and subsurface discontinuities.
2. It is highly accurate in determining reflector position and estimating size and shape like mainly TOFD (time of flight diffraction) method used for accurate sizing in mm.
3. Detailed images can be produced with automated systems
4. It can replace requirement of Radiography as per some codes (like ASME code case 2235).
5. Instant results due to electronic equipment.
6. Can be highly automated or portable.
Limitations
1. Ultrasonic Flaw detection requires experienced inspectors.
2. Extensive technical knowledge is required for the development of Ultrasonic testing procedures.
3. Parts that are rough, irregular in shape, very small or thin or not homogenous are difficult to be tested
4. Discontinuities that are preset in a shallow layer immediately beneath the surface may not be detectable.
5. Couplants are needed to provide effective transfer of ultrasonic wave energy between transducers and parts being tested.
6. Reference standards are needed, both for calibrating the equipment and for characterizing flaws.
7. Cast iron and other coarse grained materials are difficult to inspect due to low sound transmission and high signal noise.
8. Linear defects oriented parallel to the sound beam may go undetected.
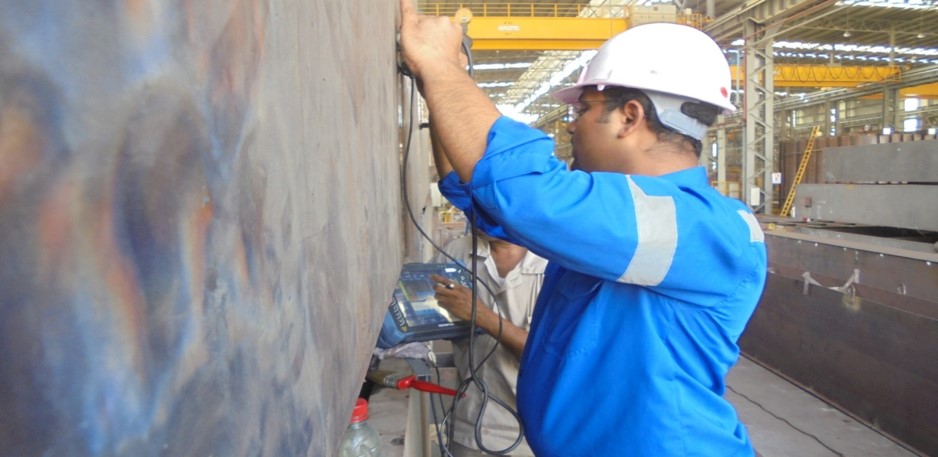
Ultrasonic Inspection facilities at UIC, Jubail, KSA.
1. Ultrasonic flaw detection equipment like mentioned below:
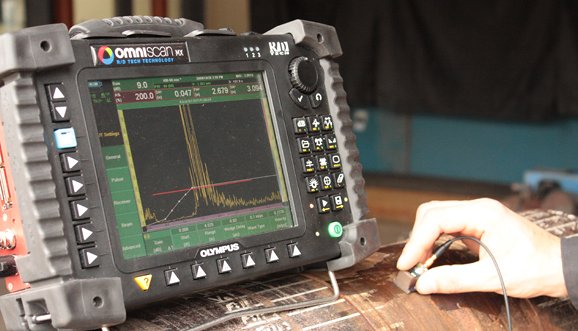
• Olympus Omniscan MX-U for manual UT & advance UT
• Olympus Omniscan MX-2 for manual UT & advance UT
• SIUI for manual UT
• Mod sonic Einstein TFT manual UT
• GE-phasor XS manual UT & advance UT
• GE-krautkramer for manual UT
2. Experienced UT inspector for carry out difficult configuration of welds.
3. Experienced in house ASNT NDT Level III and experts for providing techniques establishment, procedure preparation, approval and consultancy services
4. ASNT NDT Level III trainers for conducting in house or external NDT Level 2 training and certification courses on Ultrasonic testing and other NDT inspection methods. Read more about Ultrasonic Testing Personnel Certifications.
5. UT inspectors qualified and certified to Level II as per ASNT recommended practice SNT-TC-1A is approved & also BINDT (British institute of nondestructive testing) approved Level-II according to ISO 9712:2012 for carry out advance ultrasonic inspection like TOFD (time of flight diffraction) and PAUT (phased array ultrasonic testing).
6. NDT services throughout KSA with branches in RIYADH, JIZAN, TURAIF, JEDDAH, YANBU & head office at JUABIL.